In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, a powerful new tool has emerged to revolutionize the way we build and execute code in the browser. Enter WebAssembly (Wasm), a cutting-edge technology that promises to unlock unparalleled performance and portability for web applications. But what exactly is WebAssembly, and how does it work its magic? Join us on a journey through the intricate world of Wasm, as we unravel its mysteries and discover the endless possibilities it holds for the future of web development.
Table of Contents
- Understanding WebAssembly: A Game-Changer in Web Development
- Advantages of Using WebAssembly for Performance Optimization
- Exploring the Compatibility of WebAssembly with Different Programming Languages
- Tips for Implementing WebAssembly in Your Projects
- Q&A
- In Conclusion

Understanding WebAssembly: A Game-Changer in Web Development
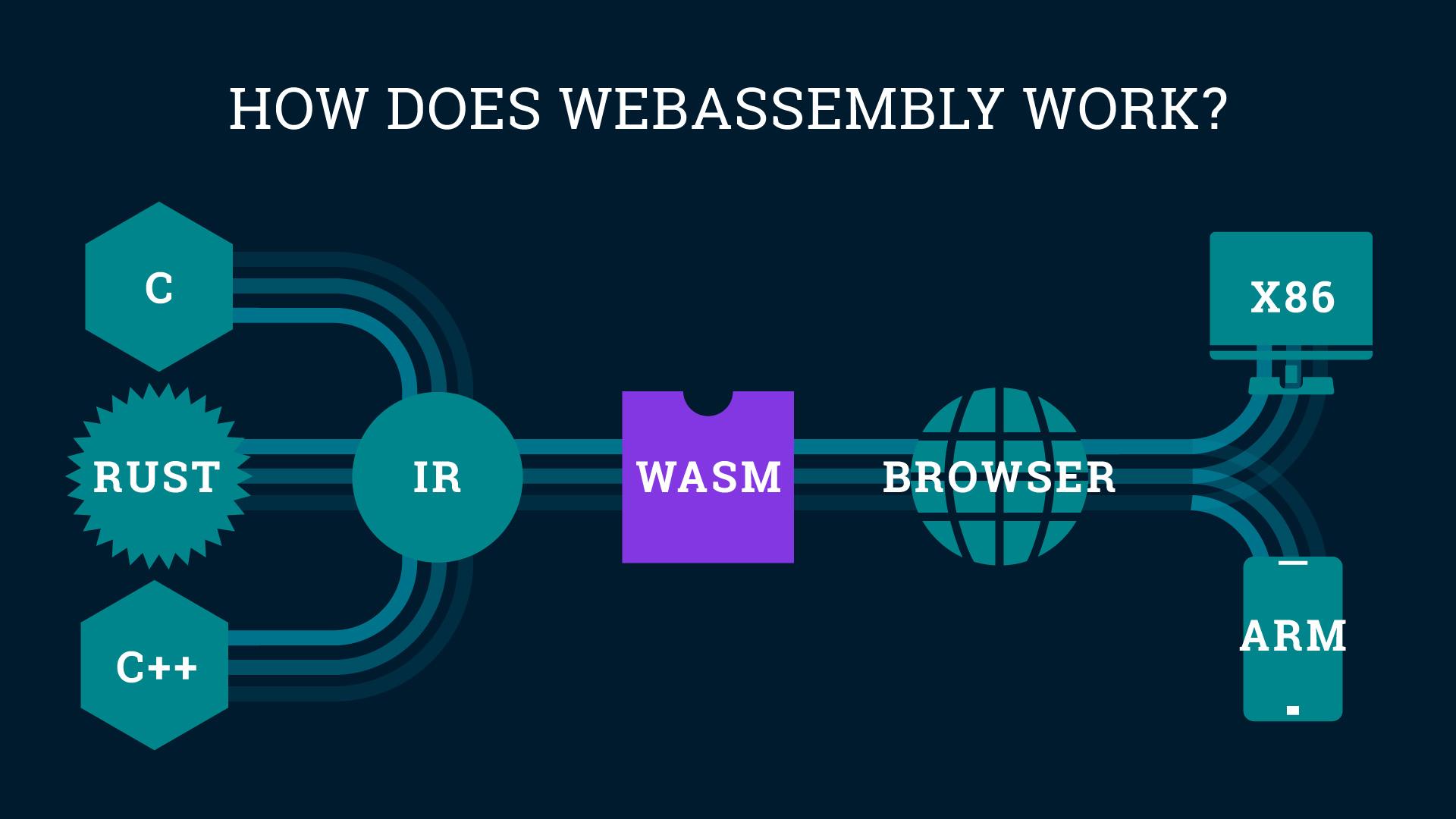
WebAssembly, also known as Wasm, is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to change the landscape of web development as we know it. It is a binary instruction format that is designed to be a compilation target for high-level languages like C, C++, and Rust, allowing for near-native performance in web applications. With WebAssembly, developers can write code in languages other than JavaScript and compile it into a format that can be executed in web browsers.
One of the key benefits of WebAssembly is its ability to improve the performance of web applications by running code at near-native speeds. This opens up a world of possibilities for developers looking to create more complex and interactive web applications. Additionally, WebAssembly is designed to be safe and secure, as it runs in a sandboxed environment within the browser. This means that malicious code cannot access sensitive user data or damage the underlying system. With WebAssembly, developers can build more efficient and secure web applications without sacrificing performance. It truly is a game-changer in the world of web development.
Advantages of Using WebAssembly for Performance Optimization
WebAssembly (Wasm) is a cutting-edge technology that enables developers to write high-performance applications for the web. By compiling code written in languages like C, C++, and Rust into a format that can be executed in the browser, WebAssembly allows for near-native performance. This means that complex tasks can be run more efficiently, resulting in faster load times and smoother user experiences.
One of the main is its ability to harness the full power of the user’s device. Since WebAssembly code is pre-compiled and runs directly on the browser’s engine, it can take advantage of multi-threading and SIMD instructions for parallel processing. This results in significant performance improvements, especially for applications that require heavy computations or graphics rendering. Additionally, WebAssembly modules are lightweight and can be easily shared and reused across different web applications, making it a versatile tool for developers looking to optimize their code for speed and efficiency.
Exploring the Compatibility of WebAssembly with Different Programming Languages
WebAssembly, also known as Wasm, is a binary instruction format that serves as a compilation target for high-level programming languages. It allows developers to write code in languages like C, C++, and Rust, and then compile that code into a binary format that can run in web browsers. This opens up a world of possibilities for web development, as it enables developers to build complex web applications that run with near-native performance.
One of the key advantages of WebAssembly is its compatibility with a wide range of programming languages. This flexibility allows developers to choose the language that best suits their needs and expertise when building web applications. Whether you prefer to work with JavaScript, Python, or Go, WebAssembly provides a bridge between these languages and the web, making it easier than ever to create fast, efficient, and feature-rich web applications.
Tips for Implementing WebAssembly in Your Projects
One key tip for implementing WebAssembly in your projects is to ensure compatibility with different browsers. WebAssembly is supported by all major browsers, but it’s essential to test your code across multiple browsers to guarantee a consistent user experience. Additionally, consider using tools like Emscripten or Rust to compile your code to WebAssembly efficiently.
Another helpful tip is to optimize your WebAssembly code for performance. By minimizing the size of your modules and reducing unnecessary computations, you can improve the speed and efficiency of your web application. Utilize techniques like tree shaking, code splitting, and bundle optimization to enhance the overall performance of your WebAssembly projects.
Q&A
Q: What is WebAssembly (Wasm) and why should we care about it?
A: WebAssembly (Wasm) is a new binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine that aims to bring native performance to the web. It allows developers to write code in languages other than JavaScript, such as C, C++, and Rust, and run it in web browsers at near-native speeds.
Q: How does WebAssembly differ from JavaScript?
A: WebAssembly is a low-level programming language, while JavaScript is a high-level language. WebAssembly is designed for performance-critical code and is not meant to replace JavaScript, but rather complement it by providing a more efficient alternative for certain tasks.
Q: What are the advantages of using WebAssembly?
A: Some advantages of using WebAssembly include improved performance, reduced load times, the ability to reuse existing code written in other languages, and increased security by running code in a sandboxed environment.
Q: How can developers start using WebAssembly in their projects?
A: Developers can start using WebAssembly in their projects by compiling their code from languages such as C, C++, or Rust into WebAssembly using tools like Emscripten or the Rust compiler. They can then integrate the WebAssembly module into their web applications using JavaScript.
Q: Is WebAssembly supported by all web browsers?
A: WebAssembly is supported by all major web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. However, support may vary depending on the version of the browser and the specific features of WebAssembly being used.
In Conclusion
WebAssembly (Wasm) is revolutionizing the way we build and run applications on the web. Its ability to provide near-native performance while maintaining cross-platform compatibility makes it a powerful tool for developers. As we continue to explore the capabilities of Wasm, we can look forward to even more innovative and efficient web applications in the future. Embrace the power of WebAssembly and discover the endless possibilities it brings to the world of web development. Happy coding!