In the fast-paced world of cloud computing, ensuring the resilience and stability of your Kubernetes clusters is essential for maintaining peak performance. One key tool in your arsenal is cluster auto-healing, a powerful feature that helps automatically detect and recover from node failures. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the ins and outs of configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing set up, equipping you with the knowledge and tools needed to keep your clusters running smoothly and efficiently. Join us on this journey as we explore the nuances of auto-healing and learn how to harness its full potential for your infrastructure.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Kubernetes Cluster Auto-Healing
- Key Components of Auto-Healing Configuration
- Best Practices for Setting Up Auto-Healing in Kubernetes
- Advanced Tips for Optimizing Auto-Healing Performance
- Q&A
- In Summary
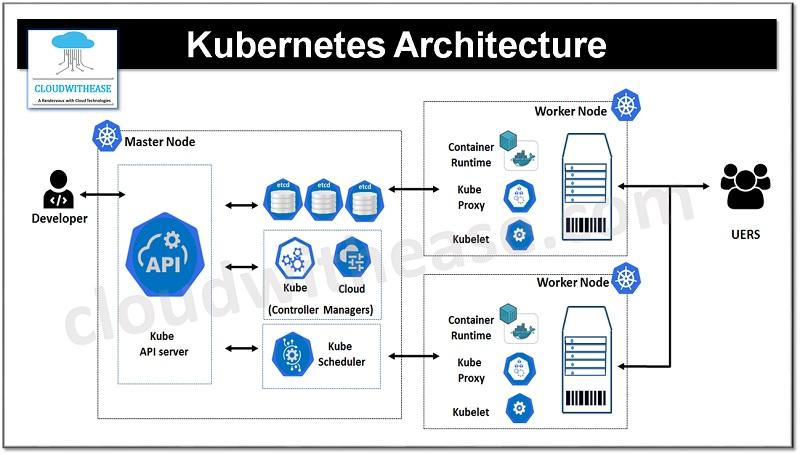
Introduction to Kubernetes Cluster Auto-Healing
Setting up Kubernetes cluster auto-healing is a crucial aspect of maintaining the stability and reliability of your cluster. By enabling auto-healing, you can ensure that your applications continue to run smoothly even in the face of unexpected failures or issues. This feature automatically detects and replaces unhealthy nodes, helping to minimize downtime and prevent disruptions to your services.
Configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing involves defining the parameters and policies that dictate how the system should respond to failures. This includes specifying conditions for node failure detection, setting up remediation actions, and fine-tuning the monitoring and alerting mechanisms. By following best practices and leveraging the power of Kubernetes auto-healing, you can enhance the resilience of your cluster and optimize the performance of your applications.

Key Components of Auto-Healing Configuration
One key component of auto-healing configuration in a Kubernetes cluster is Pod Monitoring. This feature allows the system to continuously monitor the health and status of pods within the cluster. By setting up proper monitoring rules, the system can automatically detect any unhealthy pods and take necessary actions to restart or replace them.
Another crucial component is Health Checks. Health checks enable the system to validate the health of individual pods by periodically sending requests to them. If a pod fails to respond or returns an error, the system can automatically mark it as unhealthy and trigger the auto-healing process. Properly configured health checks are essential for ensuring the reliability and stability of the Kubernetes cluster.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Pod Monitoring | Continuous monitoring of pod health and status |
| Health Checks | Validation of pod health through periodic requests |
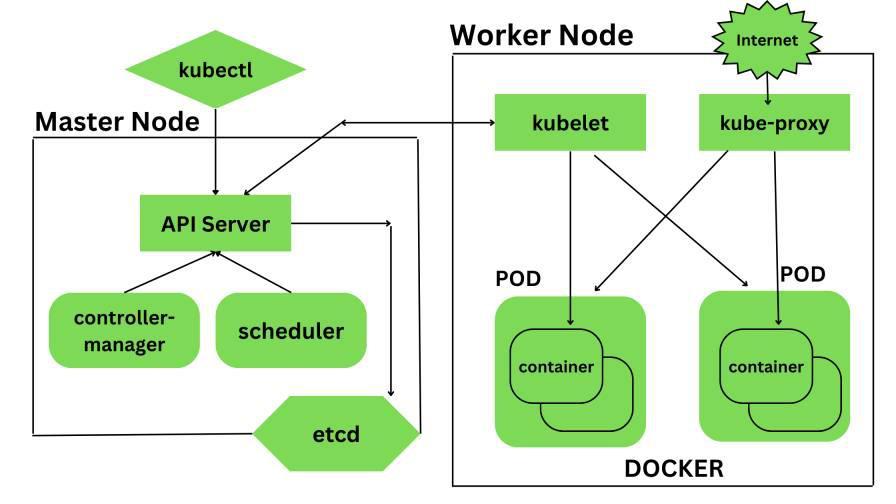
Best Practices for Setting Up Auto-Healing in Kubernetes
When setting up auto-healing in Kubernetes, it is essential to follow best practices to ensure the smooth operation of your cluster. One key practice is to carefully monitor your cluster’s health and define appropriate thresholds for triggering auto-healing actions. By regularly monitoring the health of your cluster, you can proactively address any issues before they impact your applications.
Another best practice is to use readiness and liveness probes in your pod specifications. Readiness probes allow Kubernetes to determine when a pod is ready to start receiving traffic, while liveness probes indicate whether a pod is still running correctly. By utilizing these probes effectively, you can ensure that Kubernetes can accurately determine the health status of your pods and take appropriate action when needed.
Advanced Tips for Optimizing Auto-Healing Performance
When optimizing the auto-healing performance of your Kubernetes cluster, there are several advanced tips that can help ensure your system is running smoothly and efficiently. One key tip is to carefully monitor the health of your cluster using tools like Prometheus and Grafana. By setting up alerts based on key metrics such as CPU usage, memory usage, and pod health, you can proactively address any issues before they impact your system’s performance.
Another important aspect to consider is fine-tuning the settings of your auto-healing configuration. By adjusting parameters such as the pod eviction timeout, the pod disruption budget, and the maximum number of unavailable pods allowed, you can tailor the auto-healing process to match the specific needs of your cluster. Additionally, leveraging features such as node maintenance taints and PodDisruptionBudgets can help ensure that critical workloads are not disrupted during routine maintenance tasks or node failures.
Q&A
Q: What is Kubernetes cluster auto-healing and why is it important?
A: Kubernetes cluster auto-healing is a feature that automatically detects and replaces unhealthy nodes in a cluster. It is important because it ensures the reliability and availability of applications running in the cluster.
Q: How does Kubernetes cluster auto-healing work?
A: Kubernetes cluster auto-healing works by continuously monitoring the health and status of nodes in the cluster. If a node becomes unresponsive or unhealthy, the auto-healing feature will automatically trigger the provisioning of a new node to replace it.
Q: What are the benefits of configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing?
A: Configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing provides several benefits, including improved system reliability, reduced downtime, and increased operational efficiency. It also helps to ensure high availability of applications in the cluster.
Q: What are the steps involved in configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing?
A: The steps involved in configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing include enabling the auto-healing feature in the cluster’s configuration, setting up monitoring and alerting tools, and defining rules for when and how to replace unhealthy nodes.
Q: Are there any best practices to keep in mind when configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing?
A: Some best practices to keep in mind when configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing include regularly monitoring the health of nodes, setting up proper alerts and notifications, testing the auto-healing feature regularly, and fine-tuning the configuration based on the specific requirements of the cluster.
Q: What are some common challenges faced when configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing?
A: Some common challenges faced when configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing include false positives triggering unnecessary node replacements, insufficient monitoring leading to missed alerts, and lack of proper testing resulting in unexpected behavior. It is important to address these challenges to ensure the effectiveness of the auto-healing feature.
In Summary
As we come to the end of our complete guide to configuring Kubernetes cluster auto-healing set up, we hope you have found the information provided helpful and insightful. By implementing these strategies, you can ensure the resilience and reliability of your Kubernetes clusters, ultimately leading to a more efficient and robust infrastructure. Remember, continuous monitoring and proactive measures are key to maintaining a healthy and stable environment. Thank you for joining us on this journey to mastering Kubernetes auto-healing. Happy clustering!